Categories
Product Selector
News
- Feb 12, 2024 Coriolis Mass Flow Meters - ATEX Certified CG range of high performance ATEX approved Coriolis flow meters for Liquids and Gases. ... Read more
- Jan 2, 2024 TBQSe Digital Gas Flow Meters with built-in EVC These turbine flow meters are ideal for commercial and industrial applications for measuring natural gas in pipe sizes from DN25 up to DN150.... Read more
- Oct 17, 2023 ATEX Approval for Oil Interface Meters Model H.OIL Portable oil water interface meter from Heron Instruments receives much anticipated ATEX approval for European market... Read more
Fuel Consumption and measuring it correctly
Fuel Consumption and measuring it correctly
With so many industries reliant on industrial diesel engines or diesel powered generators, fuel consumption must be assessed to ensure these perform as expected.
Healthcare facilities, education institutes, commercial industries, manufacturing industries and telecommunication and data canters require diesel generators in times of power loss. The implications of complete power loss can be catastrophic with effects ranging from costly lost production time, vital communications failures and the risks to patient’s lives and welfare in the case of health care institutions.
Fuel consumption represents the amount of fuel that is consumed by the engine or generator in a set period of time. In vehicles this is normally shown as the amount of fuel used per unit of distance. As regulations are changing with regards to lower emissions and increased efficiency, the importance of understanding fuel consumption is paramount. This is so that any fuel leakages or wastage is identified early, so that it can be remedied. It also allows the engineers to work on the efficiency of the engine, so that efforts can be introduced to improve fuel consumption.
Bell Flow Systems offer accurate measurement solutions for fuel consumption in both single pipe and differential measurement applications involving a return or recirculating fuel line. With many larger engines, the return flow of the fuel line leads back to the tank, when using just one traditional flow meter would indicate fuel consumption as far higher than it actually is. This can be adjusted using the circulation ratio, which determines the circulated quantity as a ratio to fuel consumption.
Using one appropriately sized Macnaught oval gear meter on the supply line and another Macnaught oval gear meter on the return line ensures that accurate and precise measurements of fuel consumption can be taken. When both meters are connected to one of our Fuel Consumption controllers, each line’s fuel flow will be measured, then the difference between the supply and return will be calculated to show what the engine has actually consumed. It is displayed on the screen, measured in real time and can be re-transmitted via a choice of outputs. With the addition of optional temperature sensors which would take in to account the fuels volumetric expansion, a highly accurate measurement of total flow is then calculated.
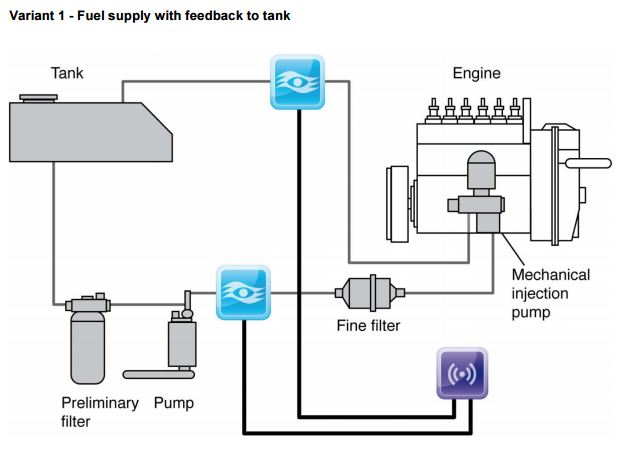
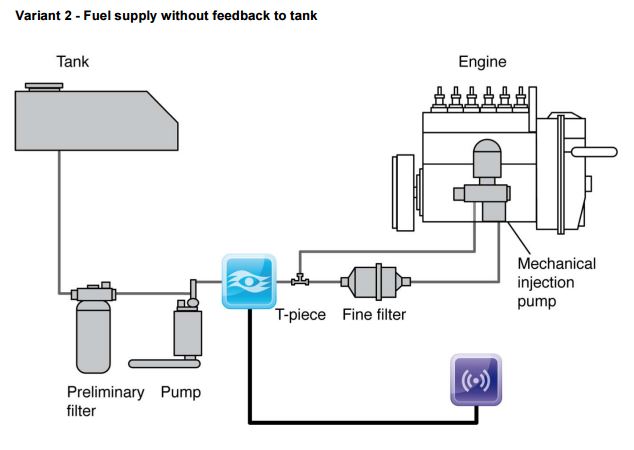
Reasons for using highly accurate “matched” fuel meters for differential measurements such as our VZO range:
Standard industrial meters often feature an accuracy of ±1%. This makes them unsuitable for differential measurements, as the following example shows:
Full load:
Supply 400 L/h Error ±1 % = nominal ±4.0 L
Return 150 L/h Error ±1 % = nominal ±1.5 L
Consumed 250 L/h Divergence = nominal ±5.5 L
Maximum divergence
Consumption = 5.5 x 100 : 250 = ±2.2 %
Idling load:
Supply 400 L/h Error ±1 % = nominal ±4.0 L
Return 360 L/h Error ±1 % = nominal ±3.6 L
Consumed 40 L/h Divergence = nominal ±7.6 L
Maximum divergence
Consumption = 7.6 x 100 : 40 = ±19 %
For an optimal result, special meters are therefore used for differential measurements. These are precisely matched to the operating conditions and are calibrated in pairs. This means that the measurement error can be significantly reduced (for example: ±0.1 % at constant flow rates on the supply side and ±0.3 % with slightly variable flow rates on the return side).
If you want us to quote your application, see here>>>, contact us at Bell Flow Systems mail@bellflowsystems.co.uk or call 01280 817304 for more information on how to measure fuel consumption accurately.

